CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1: Here you can check the CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. We have covered all questions from the exercise.
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
You will get step by step explanations of the complete Class 9 Science Chapter 1 titled Matter in Our Surroundings and You should have clear concepts on Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings for better score in exam in class 9. If you have a dream to study in science stream in future or want be an engineer then you should have a depth concept on the chapter.
After completion of the lesson, you must be looking for answers of its questions. Here you can get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings in one place, also follow NCERT Class 9 Chemistry study material to know more about Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 notes, Science.
Topics Under NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
Topics and Sub Topics in Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings:
- Matter in Our Surroundings
- Physical Nature of Matter
- Characteristics of Particles of Matter
- States of Matter
- Can Matter Change its State?
- Evaporation
You can check the complete solutions related to chapter 1 in the below section.
Questions and Answers For Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
Here you can find complete question and their answers for Class 9 Science Chapter 1
1. Which of the following are matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, smell of perfume.
Solution: Chair, air, almonds, cold drinks and smell of perfume are matter since they have mass and occupy space. Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass- in other words, matter has mass and volume.
The smell of perfume is considered as a matter since the smell of any substance (say, perfume) is the gaseous form of that substance which our olfactory system can detect (even at very low concentrations).
Hence, the smell or odour of a substance is classified as matter. However, the sense of smell does not matter. Love, hate, cold and thought are also not matter as they do not have mass and volume.
2. Give reasons for the following observation:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several meter away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Solution: The particles of hot sizzling food possess large kinetic energy and diffuse in air rapidly. Thus, the smell can reach several meter away. Whereas particles of cold food possess less kinetic energy and are not able to reach several meter away.
3. A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Solution: The particles of matter have spaces between them and the inter particle forces of attraction between liquid particles are not very strong. Hence, the force applied by diver is enough to overcome these forces of attraction.
4. What are the characteristics of particles of matter?
Solution: The characteristics of particles of matter are:
- All matter is composed of very small particles which can exist independently.
- They have spaces between
- They are continuously
- They attract each
5. The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (density = mass/volume). Arrange the following in order of increasing density – air, exhaust from chimney, honey, water, chalk, cotton, and iron
Solution:
The given substances in the increasing order of their densities can be represented as:
Exhaust from chimney < Air < Cotton < Water < Honey < Chalk < Iron
6. (a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of
(b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy, and density.
Solution: (a) Characteristics of states of matter:
|
Solid |
Liquid |
Gas |
|
Have definite shape |
Do not have a definite shape; they take the shape of the container |
Do not have a definite shape; they take the shape of the container |
|
Have a definite size or volume |
Have a definite size or volume |
Do not have a definite size or volume |
|
Negligible compressibility |
Slightly compressible |
Highly compressible |
|
Particles do not move freely |
Particles move freely but are confirmed |
Particles can move freely |
|
Particle do not move freely |
Particles move freely but are confirmed within a boundary |
Particles can move freely |
|
Property |
Solid state |
Liquid state |
Gaseous state |
|
Rigidity: |
Highly rigid |
Less rigid as compared to solids |
Not rigid |
|
Compressibility |
Negligible |
Low |
Very high |
|
Fluidity |
Do not flow |
Flow from a higher level to a low level |
Flow in all directions |
|
Filling a gas container: |
Do not need a container to contain them |
Need a container to contain them take the container in which they ate kept. |
Need a container to contain them Gases fill a container completely. |
|
Shape |
Definite |
No definite shape Liquids attain the shape of the vessel in which they are kept |
Gases do not have a definite shape |
|
Kinetic energy: |
Least kinetic energy |
More kinetic energy than solids but less than that of gases |
Maximum kinetic energy |
|
Density: |
Highest density |
Liquids have a lower density than solids but higher than that of liquids |
Lowest density |
7. Give reasons:
- A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is
- A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the
- A wooden table should be called a
- We can easily move our hand in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate
Solution:
- Due to the negligible force of attraction between the particles of gas, a gas completely fills the vessel in which it is kept. Thus, the gas particles move freely in all
- The particles of gas move randomly in all directions at high speed and therefore a gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container. The particles hit each other and also hit the walls of the container with a force. These collisions of the gas particles with the walls of the container exert pressure on the walls of the
- A wooden table has a definite shape and It is very rigid and cannot be compressed i.e., it has the characteristics of a solid. Therefore, a wooden table should be called a solid.
- The particles of the air have large intermolecular spaces and least force of attraction between them and that is why we can easily move our hand in the air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert. The particles of solid have a minimum amount of intermolecular space and maximum force of attraction between them. Thus, a greater amount of force is required to move the particles of solid.
8. Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why?
Solution: Density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance (density = mass/volume). As the volume of a substance increases, its density decreases.
Ice is a solid, but it has a cage like structure hence there is a large number of empty spaces between its particles as compared to the spaces present between the particles of water.
Therefore, the volume of ice is greater than that of water for a given mass of water. The density of ice is less than that of water. A substance with lower density than water can float on water. Therefore, ice floats on water.
9. Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale:
- 300 K
- 573 K
Solution:
- Temperature in Kelvin = Temperature in ℃+ 273 300 K = (300 – 273) = 27℃
- Temperature in Kelvin = Temperature in ℃+ 273 Temperature in Kelvin = (573 – 273) ℃ = 300℃
10. What is the physical state of water at? (a) 250℃ (b) 100℃
Solution:
- At 250℃, water exists in a gaseous
- At 100℃, water exists in both liquid and gaseous
11. For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Solution: For any substances, the temperature remains constant during a change of state. This is because all the heat supplied to increase the temperature is utilized in changing the state by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. This heat is called the latent heat. It does not contribute to increasing the temperature of the substance.
12. Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Solution: Atmospheric gases can be liquefied by increasing pressure and reducing the temperature.
13. Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Solution: A higher rate of evaporation gives a better cooling effect. If the amount of water vapour present in air (humidity) is less, then evaporation is more. On a hot dry day, the amount of water vapour present in air is less. In a desert cooler, the water inside it is made to evaporate. This leads to absorption of energy from the surroundings, thereby cooling the surroundings. Thus, water present inside the desert cooler evaporates, thereby cooling the surroundings more. That is why a desert cooler cools better on a hot dry day.
14. How does water kept in an earthen pot (make) become cool during summers?
Solution: There are many extremely small pores in an earthen pot. Through these pores, the water kept inside the pot keeps on evaporating and takes the latent heat required for vaporization from the earthen pot and remaining water. Thus, it loses heat, and this makes the water inside the pot cool.
15. Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Solution: When we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on our palm, it feels cold due to evaporation. During evaporation, particles of the liquid absorb energy from the surface of the palm. It compensates for the loss of energy and makes the surroundings cool. Hence, our palm feels cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it.
16. Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than a cup?
Solution: We can sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than a cup because of a larger surface area affecting evaporation. The larger is the surface area, more is the evaporation. Thus, evaporation is faster in a saucer causing a hot tea or milk to cool faster than in a cup.
17. What type of clothes should we wear in summers?
Solution: Clothing made of cotton are usually worn during summer since our body tend to sweat a lot. Cotton is a good absorber of water hence absorbing sweat from our body. It exposes the sweat to the atmosphere, making its evaporation faster.
During this evaporation, particles on the surface of the sweat gain energy from our body surface, making the body cool. Light coloured clothes are also a poorer absorber of heat and would be better for summer. Thus, we should wear cotton clothes and light coloured clothes in summers.
CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Questions from Textbook Excercise
1. Convert the following temperatures to Celsius
(a) 293 K
(b) 470 K
Solution: (a) We know,
Temperature in Kelvin = Temperature in ℃+ 273
293 K = (293 – 273) = 20 ℃
(b) We know,
Temperature in Kelvin = Temperature in ℃+ 273
470 K = (470 – 273) = 197 ℃
2. Convert the following temperatures to Kelvin scale.
(a) 25℃
(b) 373℃
Solution:
(a) We know,
Temperature in Kelvin = Temperature in ℃+ 273
293 K = (293 – 273)
= 20 ℃
(b) We know,
Temperature in Kelvin = Temperature in ℃+ 273
470 K = (470 – 273)
= 197 ℃
3. Give reason for the following
- Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any
- We can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres
Solution:
- Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid due to the phenomenon of Sublimation is the change of state from a solid to a gas without the intervention of a liquid state. Thus, naphthalene balls keep on forming naphthalene vapours which disappear into the air with time without leaving any solid.
- Gaseous particles possess kinetic energy and has a high speed, moving rapidly in all directions. When perfume is sprayed, the perfume molecules diffuse into the particles of air at a rapid rate and reach our nostrils. This enables us to smell the perfume from
4. Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between particles- water, sugar, and oxygen.
Solution: The increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles of water, sugar and oxygen is
Oxygen < Water < Sugar
Sugar is solid; the forces of attraction between the particles of sugar are strong.
Water is a liquid; the forces of attraction here are weaker than sugar. Oxygen is a gas; the forces of attraction are the weakest in gases.
5. What is the physical state of water at?
- 25 °C
- 0 °C
- 250 °C
Solution: At 25 °C, water is in the liquid state.
At 0 °C, water can exist as both solid and liquid.
NOTE:
At 0 °C temperature, after getting the heat equal to the latent heat of fusion, the solid form of water i.e., ice starts changing into its liquid form i.e., water.
At 250 °C, water exists in the gaseous state. At this stage, water is above the boiling point (100 °C) and due to the continuous supply of heat energy even after the boiling point, water changes to the gaseous state.
6. Give two reasons to justify-
- Water at room temperature is a
- An iron almirah is a solid at room
Solution:
- At room temperature (25℃, water is a liquid because it possesses the following characteristics of liquid:
- At room temperature (anywhere from 0℃ to 100℃), water is found in a liquid state. This is because of the weak bonds which hold water molecules together for small fractions of a second. Water molecules are constantly on the move. Therefore, at room temperature, water flows
- Water has no shape but has a fixed volume i.e., it occupies the shape of the container in which it is kept.
- An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature (25℃) because:
- It has a definite shape and volume like a solid at room
- It is rigid as solid at room
7. Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Solution: When ice is at 273 K, it will first take the heat (latent heat) from the medium to convert itself into the water as well as heat energy to attain room temperature.
In case of ice at 273 K, there will be a change in phase, so more energy will be required. In case of water at 273 K, there will be no change in phase.
Hence, less energy will be taken from the surroundings compared to ice. So, at the same temperature of 273 K, a large amount of heat will be removed by ice from the surroundings than in case of water. Therefore, ice at 273 K is more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature.
8. What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Solution: Steam possesses the additional latent heat of vaporisation. When steam comes in contact with skin and condenses to produce water, it gives out 22.5 x 105 J/kg more heat than boiling water at the same temperature. Therefore, burns produced by steam are more severe than those produced by boiling water.
9. Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its

Solution:
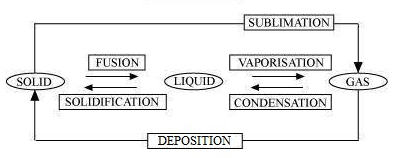
- Fusion
- Vaporisation
- Condensation
- Solidification
- Sublimation
- Deposition
We have covered the detailed guide on NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. Feel free to ask any question related to NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 1 in the comment section below.