
RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 25 Exercise 25.1: You can get the detailed solutions PDF for RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 25 Exercise 25.1. These solutions are created by our experts which will help students for their Class 9 exams.
Download RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 25 Exercise 25.1
RD-SHARMA-Solutions-Class-9-Maths-Chapter-25-Ex-25.1
Access RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 25 Exercise 25.1
Question 1: A coin is tossed 1000 times with the following sequence:
Head: 455, Tail: 545
Compute the probability of each event.
Solution:
Coin is tossed 1000 times, which means, number of trials are 1000.
Let us consider, event of getting head and event of getting tail be E and F respectively.
Number of favorable outcome = Number of trials in which the E happens = 455
So, Probability of E = (Number of favorable outcome) / (Total number of trials)
P(E) = 455/1000 = 0.455
Similarly,
Number of favorable outcome = Number of trials in which the F happens = 545
Probability of the event getting a tail, P(F) = 545/1000 = 0.545
Question 2: Two coins are tossed simultaneously 500 times with the following frequencies of different outcomes:
Two heads: 95 times
One tail: 290 times
No head : 115 times
Find the probability of occurrence of each of these events.
Solution:
We know that, Probability of any event = (Number of favorable outcome) / (Total number of trials)
Total number of trials = 95 + 290 + 115 = 500
Now,
P(Getting two heads) = 95/500 = 0.19
P(Getting one tail) = 290/500 = 0.58
P(Getting no head) = 115/500 = 0.23
Question 3: Three coins are tossed simultaneously 100 times with the following frequencies of different outcomes:
| Outcome | No head | One head | Two heads | Three heads |
| Frequency | 14 | 38 | 36 | 12 |
If the three coins are simultaneously tossed again, compute the probability of:
(i) 2 heads coming up
(ii) 3 heads coming up
(iii) At least one head coming up
(iv) Getting more heads than tails
(v) Getting more tails than heads
Solution:
We know, Probability of an event = (Number of Favorable outcomes) / (Total Numbers of outcomes)
In this case, total numbers of outcomes = 100.
(i) Probability of 2 Heads coming up = 36/100 = 0.36
(ii) Probability of 3 Heads coming up = 12/100 = 0.12
(iii) Probability of at least one head coming up = (38+36+12) / 100 = 86/100 = 0.86
(iv) Probability of getting more Heads than Tails = (36+12)/100 = 48/100 = 0.48
(v) Probability of getting more tails than heads = (14+38) / 100 = 52/100 = 0.52
Question 4: 1500 families with 2 children were selected randomly, and the following data were recorded:
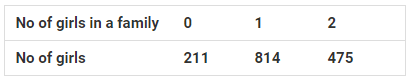
If a family is chosen at random, compute the probability that it has:
(i) No girl (ii) 1 girl (iii) 2 girls (iv) At most one girl (v) More girls than boys
Solution:
We know, Probability of an event = (Number of Favorable outcomes) / (Total Numbers of outcomes)
In this case, total numbers of outcomes = 211 + 814 + 475 = 1500.
(Here, total numbers of outcomes = total number of families)
(i) Probability of having no girl = 211/1500 = 0.1406
(ii) Probability of having 1 girl = 814/1500 = 0.5426
(iii) Probability of having 2 girls = 475/1500 = 0.3166
(iv) Probability of having at the most one girl = (211+814) /1500 = 1025/1500 = 0.6833
(v) Probability of having more girls than boys = 475/1500 = 0.31
Question 5: In a cricket match, a batsman hits a boundary 6 times out of 30 balls he plays. Find the probability that on a ball played:
(i) He hits boundary (ii) He does not hit a boundary.
Solution:
Total number of balls played by a player = 30
Number of times he hits a boundary = 6
Number of times he does not hit a boundary = 30 – 6 = 24
We know, Probability of an event = (Number of Favorable outcomes) / (Total Numbers of outcomes)
Now,
(i) Probability (he hits boundary) = (Number of times he hit a boundary) / (Total number of balls he played)
= 6/30 = 1/5
(ii) Probability that the batsman does not hit a boundary = 24/30 = 4/5
Question 6: The percentage of marks obtained by a student in monthly unit tests are given below:

Find the probability that the student gets
(i) More than 70% marks
(ii) Less than 70% marks
(iii) A distinction
Solution:
Total number of unit tests taken = 5
We know, Probability of an event = (Number of Favorable outcomes) / (Total Numbers of outcomes)
(i) Number of times student got more than 70% = 3
Probability (Getting more than 70%) = 3/5 = 0.6
(ii) Number of times student got less than 70% = 2
Probability (Getting less than 70%) = 2/5 = 0.4
(iii) Number of times student got a distinction = 1
[Marks more than 75%]
Probability (Getting a distinction) = 1/5 = 0.2
Question 7: To know the opinion of the students about Mathematics, a survey of 200 students were conducted. The data was recorded in the following table:
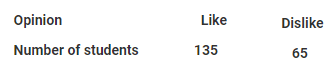
Find the probability that student chosen at random:
(i) Likes Mathematics (ii) Does not like it.
Solution:
Total number of students = 200
Students like mathematics = 135
Students dislike Mathematics = 65
We know, Probability of an event = (Number of Favorable outcomes) / (Total Numbers of outcomes)
(i) Probability (Student likes mathematics) = 135/200 = 0.675
(ii) Probability (Student does not like mathematics) = 65/200 = 0.325
We have included all the information regarding CBSE RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 25 Exercise 25.1. If you have any query feel free to ask in the comment section.
FAQ: RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 25 Exercise 25.1
Can I open RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 25 Exercise 25.1 PDF on my smartphone?
Yes, you can open RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 25 Exercise 25.1 PDF on any device.
Can I download RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 25 Exercise 25.1 PDF free?
Yes, you can download RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 25 Exercise 25.1 PDF free.
What are the benefits of studying RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions?
By practicing RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions, students can earn higher academic grades. Our experts solve these solutions with utmost accuracy to help students in their studies.
Is RD Sharma enough for Class 12 Maths?
RD Sharma is a good book that gives you thousands of questions to practice.
