
RD Sharma Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1: The key topics covered in exercise 6.1 are the determinant of a square matrix of order 1, 2, 3, and 4, singular matrix, minors, and cofactors of specified determinants. Students can use this exercise as a model of reference to strengthen their conceptual knowledge and comprehend the various methods utilised to solve problems. RD Sharma Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 are available in PDF format. The RD Sharma Class 12 Solutions were designed by Kopykitab’s Math experts in order to boost students’ confidence, which is important in board exams.
Download RD Sharma Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 Free PDF
RD Sharma Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1
Access answers to Maths RD Sharma Solutions For Class 12 Chapter 6 – Determinants Exercise 6.1 Important Questions With Solution
1. Write the minors and cofactors of each element of the first column of the following matrices and hence evaluate the determinant in each case:
Solution:
(i) Let Mij and Cij represent the minor and co–factor of an element, where i and j represent the row and column. The minor of the matrix can be obtained for a particular element by removing the row and column where the element is present. Then finding the absolute value of the matrix newly formed.
Also, Cij = (–1)i+j × Mij
Given,
![]()
From the given matrix we have,
M11 = –1
M21 = 20
C11 = (–1)1+1 × M11
= 1 × –1
= –1
C21 = (–1)2+1 × M21
= 20 × –1
= –20
Now expanding along the first column we get
|A| = a11 × C11 + a21× C21
= 5× (–1) + 0 × (–20)
= –5
(ii) Let Mij and Cij represents the minor and co–factor of an element, where i and j represent the row and column. The minor of matrix can be obtained for particular element by removing the row and column where the element is present. Then finding the absolute value of the matrix newly formed.
Also, Cij = (–1)i+j × Mij
Given
![]()
From the above matrix we have
M11 = 3
M21 = 4
C11 = (–1)1+1 × M11
= 1 × 3
= 3
C21 = (–1)2+1 × 4
= –1 × 4
= –4
Now expanding along the first column we get
|A| = a11 × C11 + a21× C21
= –1× 3 + 2 × (–4)
= –11
(iii) Let Mij and Cij represents the minor and co–factor of an element, where i and j represent the row and column. The minor of the matrix can be obtained for a particular element by removing the row and column where the element is present. Then finding the absolute value of the matrix newly formed.
Also, Cij = (–1)i+j × Mij
Given,

M31 = –3 × 2 – (–1) × 2
M31 = –4
C11 = (–1)1+1 × M11
= 1 × –12
= –12
C21 = (–1)2+1 × M21
= –1 × –16
= 16
C31 = (–1)3+1 × M31
= 1 × –4
= –4
Now expanding along the first column we get
|A| = a11 × C11 + a21× C21+ a31× C31
= 1× (–12) + 4 × 16 + 3× (–4)
= –12 + 64 –12
= 40
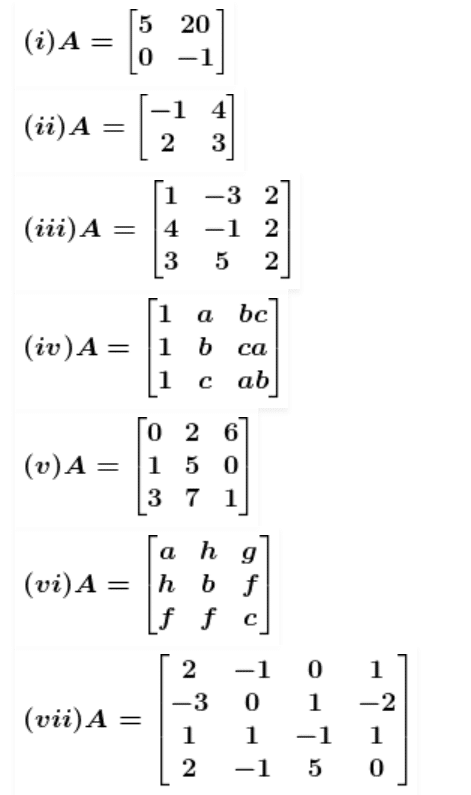
(iv) Let Mij and Cij represents the minor and co–factor of an element, where i and j represent the row and column. The minor of the matrix can be obtained for a particular element by removing the row and column where the element is present. Then finding the absolute value of the matrix newly formed.
Also, Cij = (–1)i+j × Mij
Given,
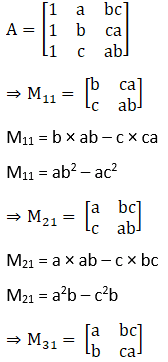
M31 = a × c a – b × bc
M31 = a2c – b2c
C11 = (–1)1+1 × M11
= 1 × (ab2 – ac2)
= ab2 – ac2
C21 = (–1)2+1 × M21
= –1 × (a2b – c2b)
= c2b – a2b
C31 = (–1)3+1 × M31
= 1 × (a2c – b2c)
= a2c – b2c
Now expanding along the first column we get
|A| = a11 × C11 + a21× C21+ a31× C31
= 1× (ab2 – ac2) + 1 × (c2b – a2b) + 1× (a2c – b2c)
= ab2 – ac2 + c2b – a2b + a2c – b2c
(v) Let Mij and Cij represents the minor and co–factor of an element, where i and j represent the row and column. The minor of matrix can be obtained for particular element by removing the row and column where the element is present. Then finding the absolute value of the matrix newly formed.
Also, Cij = (–1)i+j × Mij
Given,
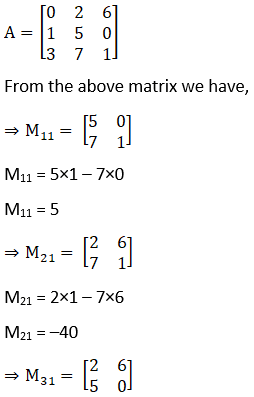
M31 = 2×0 – 5×6
M31 = –30
C11 = (–1)1+1 × M11
= 1 × 5
= 5
C21 = (–1)2+1 × M21
= –1 × –40
= 40
C31 = (–1)3+1 × M31
= 1 × –30
= –30
Now expanding along the first column we get
|A| = a11 × C11 + a21× C21+ a31× C31
= 0× 5 + 1 × 40 + 3× (–30)
= 0 + 40 – 90
= 50
(vi) Let Mij and Cij represents the minor and co–factor of an element, where i and j represent the row and column. The minor of matrix can be obtained for particular element by removing the row and column where the element is present. Then finding the absolute value of the matrix newly formed.
Also, Cij = (–1)i+j × Mij
Given,
M31 = h × f – b × g
M31 = hf – bg
C11 = (–1)1+1 × M11
= 1 × (bc– f2)
= bc– f2
C21 = (–1)2+1 × M21
= –1 × (hc – fg)
= fg – hc
C31 = (–1)3+1 × M31
= 1 × (hf – bg)
= hf – bg
Now expanding along the first column we get
|A| = a11 × C11 + a21× C21+ a31× C31
= a× (bc– f2) + h× (fg – hc) + g× (hf – bg)
= abc– af2 + hgf – h2c +ghf – bg2
(vii) Let Mij and Cij represents the minor and co–factor of an element, where i and j represent the row and column. The minor of matrix can be obtained for particular element by removing the row and column where the element is present. Then finding the absolute value of the matrix newly formed.
Also, Cij = (–1)i+j × Mij
Given,
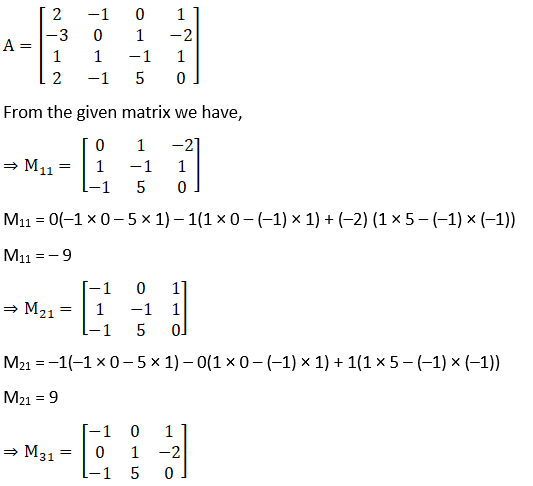
M31 = –1(1 × 0 – 5 × (–2)) – 0(0 × 0 – (–1) × (–2)) + 1(0 × 5 – (–1) × 1)
M31 = –9
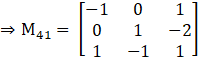
M41 = –1(1×1 – (–1) × (–2)) – 0(0 × 1 – 1 × (–2)) + 1(0 × (–1) – 1 × 1)
M41 = 0
C11 = (–1)1+1 × M11
= 1 × (–9)
= –9
C21 = (–1)2+1 × M21
= –1 × 9
= –9
C31 = (–1)3+1 × M31
= 1 × –9
= –9
C41 = (–1)4+1 × M41
= –1 × 0
= 0
Now expanding along the first column we get
|A| = a11 × C11 + a21× C21+ a31× C31 + a41× C41
= 2 × (–9) + (–3) × –9 + 1 × (–9) + 2 × 0
= – 18 + 27 –9
= 0
2. Evaluate the following determinants:

Solution:
(i) Given
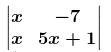
⇒ |A| = x (5x + 1) – (–7) x
|A| = 5x2 + 8x
(ii) Given
![]()
⇒ |A| = cos θ × cos θ – (–sin θ) x sin θ
|A| = cos2θ + sin2θ
We know that cos2θ + sin2θ = 1
|A| = 1
(iii) Given
![]()
⇒ |A| = cos15° × cos75° + sin15° x sin75°
We know that cos (A – B) = cos A cos B + Sin A sin B
By substituting this we get, |A| = cos (75 – 15)°
|A| = cos60°
|A| = 0.5
(iv) Given
![]()
⇒ |A| = (a + ib) (a – ib) – (c + id) (–c + id)
= (a + ib) (a – ib) + (c + id) (c – id)
= a2 – i2 b2 + c2 – i2 d2
We know that i2 = -1
= a2 – (–1) b2 + c2 – (–1) d2
= a2 + b2 + c2 + d2
3. Evaluate:
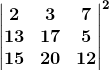
Solution:
Since |AB|= |A||B|
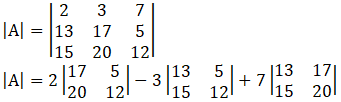
= 2(17 × 12 – 5 × 20) – 3(13 × 12 – 5 × 15) + 7(13 × 20 – 15 × 17)
= 2 (204 – 100) – 3 (156 – 75) + 7 (260 – 255)
= 2×104 – 3×81 + 7×5
= 208 – 243 +35
= 0
Now |A|2 = |A|×|A|
|A|2= 0
4. Show that
![]()
Solution:
Given
![]()
Let the given determinant as A
Using sin (A+B) = sin A × cos B + cos A × sin B
⇒ |A| = sin 10° × cos 80° + cos 10° x sin 80°
|A| = sin (10 + 80)°
|A| = sin90°
|A| = 1
Hence Proved
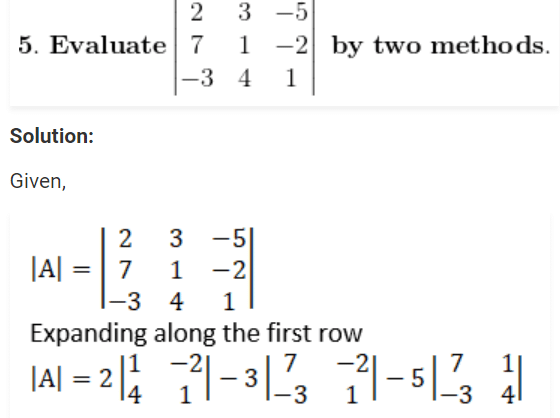
= 2(1 × 1 – 4 × (–2)) – 3(7 × 1 – (–2) × (–3)) – 5(7 × 4 – 1 × (–3))
= 2(1 + 8) – 3(7 – 6) – 5(28 + 3)
= 2 × 9 – 3 × 1 – 5 × 31
= 18 – 3 – 155
= –140
Now by expanding along the second column
![]()
= 2(1 × 1 – 4 × (–2)) – 7(3 × 1 – 4 × (–5)) – 3(3 × (–2) – 1 × (–5))
= 2 (1 + 8) – 7 (3 + 20) – 3 (–6 + 5)
= 2 × 9 – 7 × 23 – 3 × (–1)
= 18 – 161 +3
= –140
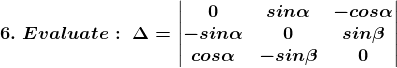
Solution:
Given
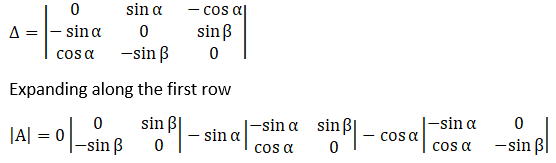
⇒ |A| = 0 (0 – sinβ (–sinβ)) –sinα (–sinα × 0 – sinβ cosα) – cosα ((–sinα) (–sinβ) – 0 × cosα)
|A| = 0 + sinα sinβ cosα – cosα sinα sinβ
|A| = 0
We have provided complete details of RD Sharma Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1. If you have any queries related to CBSE Class 12 Exam, feel free to ask us in the comment section below.
FAQs on RD Sharma Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1
What are the advantages of using RD Sharma Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1?
Referring to RD Sharma Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 will provide students a good understanding of the type of questions that might be asked in the Class 12 board exam from the chapter.
Where can I get RD Sharma Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 Free PDF?
You can get RD Sharma Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 Free PDF from the above article.
How many questions are there in RD Sharma Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1?
There are a total of 12 questions in RD Sharma Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1.
